No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 May 2021
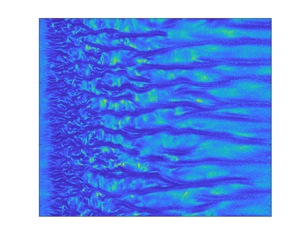
This study presents an innovative approach towards the generation and decay of turbulence in the Taylor–Couette system. The outer cylinder was brought to an abrupt stoppage that generated turbulence in the system, which was initially in the laminar flow regime. Two complementary experimental approaches, namely visualizations and stereo-particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements, were used to better understand the presented phenomenon for only external cylinder rotation. A moving time average technique was developed due to the continuous change in the length scales throughout the generation and decay process. The different stages of the generation and decay of turbulence were described and characterized through dynamic quantities such as the kinetic energy. This new approach towards the generation and decay of turbulence in the Taylor–Couette flow should help significantly in future endeavours.