Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 December 2003
Introduction. For the micropropagation of woody species, contamination of in vitro cultured explants is a constant problem, which can compromise the development of the technique. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effects of an antibiotic and a fungicide on surface and endophytic microorganisms associated with Annona cauliflora, A. bahiensis and A. glabra (Annonaceae) tissue culture. Materials and methods. Our work made it possible to compare a standard disinfection of in vitro cultured explants and the use of either a commercial fungicide, Benlate 500 (50% of benomyl) at (0.0, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0) ${\rm g} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$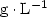 , or an antibiotic, ampicillin at (0.0, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0) ${\rm mg} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$
, or an antibiotic, ampicillin at (0.0, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0) ${\rm mg} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$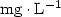 . Results. The study revealed considerable variations in the infection rates within species and according to the concentrations of benomyl and ampicillin used. Benomyl was effective at cleaning leaf segments, and, at a concentration of 1.0 ${\rm g} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$
. Results. The study revealed considerable variations in the infection rates within species and according to the concentrations of benomyl and ampicillin used. Benomyl was effective at cleaning leaf segments, and, at a concentration of 1.0 ${\rm g} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$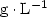 , this fungicide was sufficient to eliminate all fungi. Ampicillin treatments at (0.0 to 4.0) ${\rm mg} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$
, this fungicide was sufficient to eliminate all fungi. Ampicillin treatments at (0.0 to 4.0) ${\rm mg} \cdot {\rm L}^{-1}$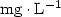 were ineffective at controlling bacterial contamination. Conclusion. Referring to the difficulty in obtaining an aseptic in vitro culture starting from a woody species, the average number of healthy explants obtained after the disinfection of foliar explants of Annona sp. using the antimicrobial substances tested was significant. Further studies to evaluate the effects of the concentration of chemicals on in vitro plant regeneration for Annona species are needed to clarify the relationship between the concentration and phytotoxic effect of chemicals.
were ineffective at controlling bacterial contamination. Conclusion. Referring to the difficulty in obtaining an aseptic in vitro culture starting from a woody species, the average number of healthy explants obtained after the disinfection of foliar explants of Annona sp. using the antimicrobial substances tested was significant. Further studies to evaluate the effects of the concentration of chemicals on in vitro plant regeneration for Annona species are needed to clarify the relationship between the concentration and phytotoxic effect of chemicals.