Article contents
698 – Urinary Tract Infection and Mental Illness
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 April 2020
Abstract
It is well known that mental illneses are associated with higher prevalence of somatic disorders when compared to the general population. We observed that, at the time of admission to the Acute Psychiatric Unit (APU) at our Hospital, many patients have associated urinary tract infection.
To determine the characteristics of patients that present with urinary tract infection on admission to the APU
From all admissions to the APU during 2011, patients with urinalysis, sediment and culture suggesting urinary tract infection were recruited for this study.
83 out of the 229 patients admitted to the APU had urinary tract infection at the moment of admission. Most common psychiatric diagnoses in patients with urinary tract infection were: mood disorders (37.35%), psychotic disorders (22.89%) and personality disorders (14.46%) Of these 83 patients, 72.29% had a history of previous psychiatric admissions and 91.67% had a new admission with an associated urinary tract infection.
Figure
[readmissions]
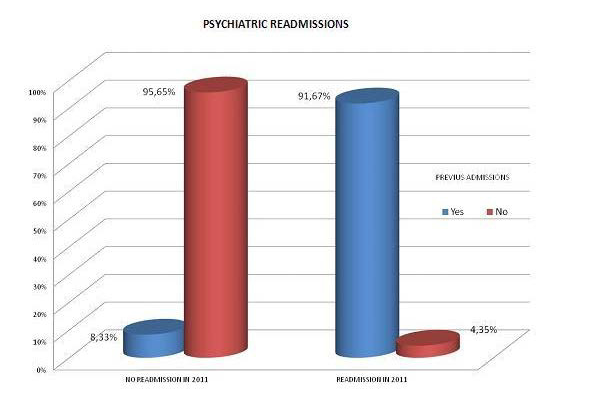
A high percentage of patients admitted to our APU have recurrent urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections may play a negative impact on their psychopathological evolution and may be associated with the need for hospital admission.
- Type
- Abstract
- Information
- European Psychiatry , Volume 28 , Issue S1: Abstracts of the 21th European Congress of Psychiatry , 2013 , 28-E214
- Copyright
- Copyright © European Psychiatric Association 2013
- 2
- Cited by



Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.