No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Dust in the SINGS Galaxy Sample
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 October 2008
Abstract
Dust models have been applied to interpret the IR emission from65 galaxies in the SINGS galaxy survey, allowing dust masses, PAH fractions,and starlight intensities to be determined. The dust models reproduce theglobal SEDs without requiring “cold” (T $\lesssim$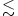 12 K) dust. The bulk of theIR emission appears to be radiated by dust in the diffuse ISM,with starlight intensities similar to the intensity in the solar neighborhood.A fraction fPDR of the IR emission is radiated by dust in regions ofhigh starlight intensities (e.g., PDRs), with median fPDR = 0.08.The dust composition is characterized by qPAH, the fraction ofthe dust mass contributed by PAHs with <103 C atoms.Galaxies with metallicities Z/Z๏ < 0.2 tend to have qPAH $\lesssim$
12 K) dust. The bulk of theIR emission appears to be radiated by dust in the diffuse ISM,with starlight intensities similar to the intensity in the solar neighborhood.A fraction fPDR of the IR emission is radiated by dust in regions ofhigh starlight intensities (e.g., PDRs), with median fPDR = 0.08.The dust composition is characterized by qPAH, the fraction ofthe dust mass contributed by PAHs with <103 C atoms.Galaxies with metallicities Z/Z๏ < 0.2 tend to have qPAH $\lesssim$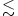 0.01, but galaxies with Z/Z๏ > 0.4 have qPAH = 0.02 - 0.05.Over the entire sample, with Z/Z๏ ranging from 0.1 to 1, theobservations are consistent with a constant fraction of interstellarmetals being in dust, with Mdust/MH ≈ 0.01(Z/Z๏).
0.01, but galaxies with Z/Z๏ > 0.4 have qPAH = 0.02 - 0.05.Over the entire sample, with Z/Z๏ ranging from 0.1 to 1, theobservations are consistent with a constant fraction of interstellarmetals being in dust, with Mdust/MH ≈ 0.01(Z/Z๏).
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- European Astronomical Society Publications Series , Volume 31: Far-Infrared Workshop 2007 , 2008 , pp. 137 - 142
- Copyright
- © EAS, EDP Sciences, 2008


