Article contents
Perturbation Analysis of Orthogonal Least Squares
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 March 2019
Abstract
The Orthogonal Least Squares (OLS) algorithm is an efficient sparse recovery algorithm that has received much attention in recent years. On one hand, this paper considers that the OLS algorithm recovers the supports of sparse signals in the noisy case. We show that the OLS algorithm exactly recovers the support of 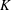 $K$-sparse signal
$K$-sparse signal  $\boldsymbol{x}$ from
$\boldsymbol{x}$ from 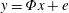 $\boldsymbol{y}=\boldsymbol{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}}\boldsymbol{x}+\boldsymbol{e}$ in
$\boldsymbol{y}=\boldsymbol{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}}\boldsymbol{x}+\boldsymbol{e}$ in 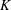 $K$ iterations, provided that the sensing matrix
$K$ iterations, provided that the sensing matrix 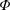 $\boldsymbol{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}}$ satisfies the restricted isometry property (RIP) with restricted isometry constant (RIC)
$\boldsymbol{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}}$ satisfies the restricted isometry property (RIP) with restricted isometry constant (RIC) 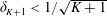 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{K+1}<1/\sqrt{K+1}$, and the minimum magnitude of the nonzero elements of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{K+1}<1/\sqrt{K+1}$, and the minimum magnitude of the nonzero elements of  $\boldsymbol{x}$ satisfies some constraint. On the other hand, this paper demonstrates that the OLS algorithm exactly recovers the support of the best
$\boldsymbol{x}$ satisfies some constraint. On the other hand, this paper demonstrates that the OLS algorithm exactly recovers the support of the best 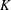 $K$-term approximation of an almost sparse signal
$K$-term approximation of an almost sparse signal  $\boldsymbol{x}$ in the general perturbations case, which means both
$\boldsymbol{x}$ in the general perturbations case, which means both 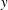 $\boldsymbol{y}$ and
$\boldsymbol{y}$ and 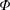 $\boldsymbol{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}}$ are perturbed. We show that the support of the best
$\boldsymbol{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}}$ are perturbed. We show that the support of the best 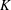 $K$-term approximation of
$K$-term approximation of  $\boldsymbol{x}$ can be recovered under reasonable conditions based on the restricted isometry property (RIP).
$\boldsymbol{x}$ can be recovered under reasonable conditions based on the restricted isometry property (RIP).
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Canadian Mathematical Society 2019
Footnotes
W. Chen is the corresponding author. This work was supported by the NSF of China (No. 11871109) and NSAF (Grant No. U1830107).
References
- 3
- Cited by


