Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
G will denote a finite (or infinite) group of order n. In a normal multiplication table (n.m.t.) of G (7, 8, 9, 12) all entries in one diagonal are equal to e (the identity of G), and if the entry on the intersection of the ith column and jth row is gi,j ∈ G, then

The following is a n.m.t. of Z6 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}:
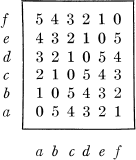
Remark. The cyclic groups Zn will always be written in additive notation. The table is uniquely defined by every one of its columns, in particular by the first.