Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 June 2022
We consider fragments of uniform reflection for formulas in the analytic hierarchy over theories of second order arithmetic. The main result is that for any second order arithmetic theory 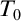 $T_0$
extending
$T_0$
extending  $\mathsf {RCA}_0$
and axiomatizable by a
$\mathsf {RCA}_0$
and axiomatizable by a 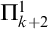 $\Pi ^1_{k+2}$
sentence, and for any
$\Pi ^1_{k+2}$
sentence, and for any 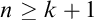 $n\geq k+1$
,
$n\geq k+1$
, 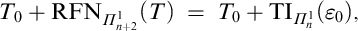 $$\begin{align*}T_0+ \mathrm{RFN}_{\varPi^1_{n+2}}(T) \ = \ T_0 + \mathrm{TI}_{\varPi^1_n}(\varepsilon_0), \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}T_0+ \mathrm{RFN}_{\varPi^1_{n+2}}(T) \ = \ T_0 + \mathrm{TI}_{\varPi^1_n}(\varepsilon_0), \end{align*}$$
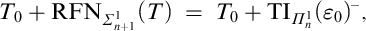 $$\begin{align*}T_0+ \mathrm{RFN}_{\varSigma^1_{n+1}}(T) \ = \ T_0+ \mathrm{TI}_{\varPi^1_n}(\varepsilon_0)^{-}, \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}T_0+ \mathrm{RFN}_{\varSigma^1_{n+1}}(T) \ = \ T_0+ \mathrm{TI}_{\varPi^1_n}(\varepsilon_0)^{-}, \end{align*}$$
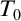 $T_0$
augmented with full induction, and
$T_0$
augmented with full induction, and 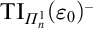 $\mathrm {TI}_{\varPi ^1_n}(\varepsilon _0)^{-}$
denotes the schema of transfinite induction up to
$\mathrm {TI}_{\varPi ^1_n}(\varepsilon _0)^{-}$
denotes the schema of transfinite induction up to 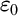 $\varepsilon _0$
for
$\varepsilon _0$
for 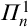 $\varPi ^1_n$
formulas without set parameters.
$\varPi ^1_n$
formulas without set parameters.