Introduction
The Antarctic Peninsula is the region of the Antarctic experiencing the fastest environmental changes (Convey & Peck Reference Convey and Peck2019) and greatest local human impact (Tin et al. Reference Tin, Liggett, Maher and Lamers2014). Loss of sea ice and the reduction in the length of the sea-ice season (Schofield et al. Reference Schofield, Brown, Kohut, Nardelli, Saba, Waite and Ducklow2018, Vorrath et al. Reference Vorrath, Müller, Rebolledo, Cárdenas, Shi and Esper2020), rapid glacier contraction (Silva et al. Reference Silva, Arigony-Neto, Braun, Espinoza, Costi and Janã2020), increased ice-free land (Lee et al. Reference Lee, Raymond, Bracegirdle, Chadès, Fuller, Shaw and Terauds2017), shifts in plankton communities (Schofield et al. Reference Schofield, Brown, Kohut, Nardelli, Saba, Waite and Ducklow2018, Kim & Kim Reference Kim and Kim2021, Schultz et al. Reference Schultz, Doney, Hauck, Kavanaugh and Schofield2021), probable biomass reduction and contraction in the southward distribution of krill (Atkinson et al. Reference Atkinson, Hill, Pakhomov, Siegel, Reiss and Loeb2019, Trathan et al. Reference Trathan, Warwick-Evans, Young, Friedlaender, Kim and Kokubun2022) are some of the observed environmental changes caused by warming. Increased fishing concentration (Nicol et al. Reference Nicol, Foster and Kawaguchi2012, Trathan et al. Reference Trathan, Warwick-Evans, Young, Friedlaender, Kim and Kokubun2022, Santa Cruz et al. Reference Santa Cruz, Krüger and Cárdenas2022) and increased human presence due to the intensification of tourism and scientific activities (Chown et al. Reference Chown, Lee, Hughes, Barnes, Barrett and Bergstrom2012, Bender et al. Reference Bender, Crosbie and Lynch2016) have led to the contamination of several areas through the release of synthetic debris (Tirelli et al. Reference Tirelli, Suaria, Lusher, Rocha-Santos, Costa and Mouneyrac2020, Finger et al. Reference Finger, Corá, Convey, Cruz, Petry and Krüger2021) and wastewater effluents, burning of fossil fuels, waste incineration and accidental spillage (Bargagli Reference Bargagli2008). While it is important to continuously track these changes, it is challenging for researchers to simultaneously cover a substantial number of vulnerable areas.
Marine top predators have been considered as tools for monitoring ecosystem changes due to their large-scale distribution and because they amplify trophic information across multiple spatiotemporal scales (Sergio et al. Reference Sergio, Caro, Brown, Clucas, Hunter and Ketchum2008, Hazen et al. Reference Hazen, Abrahms, Brodie, Carroll, Jacox and Savoca2019). Seabirds, given their habitat associations (Tam et al. Reference Tam, Link, Rossberg, Rogers, Levin and Rochet2017, Velarde et al. Reference Velarde, ANderson and Ezcurra2019, Krüger Reference Krüger, Ramos and Pereira2022) and easier access in comparison to other groups of marine top predators, have been proposed as optimal ocean sentinels (Lascelles et al. Reference Lascelles, Langham, Ronconi and Reid2012, Krüger Reference Krüger, Ramos and Pereira2022).
For instance, the strong associations of emperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) with sea ice make them sentinels of climate change in Antarctica (Jenouvrier et al. Reference Jenouvrier, Che-Castaldo, Wolf, Holland, Labrousse and LaRue2021), while krill-specialist Pygoscelis spp. penguins can indicate the state of krill populations (Lynnes et al. Reference Lynnes, Reid and Croxall2004). On the other hand, population-level generalist seabird species are usually associated with a wide range of environmental conditions and/or habitats and can act as monitors of human impacts across large spatial scales. Albatrosses, for example, have been suggested as useful sentinels of illegal, unreported and unregulated (IUU) fishing in the mid-latitudes of the Southern Ocean due to their wide oceanic distribution and propensity to interact with fishing vessels (Weimerskirch et al. Reference Weimerskirch, Collet, Corbeau, Pajot, Hoarau and Marteau2020).
Southern giant petrels (SGPs; Macronectes giganteus) are large (3.0–5.5 kg), avian generalist top predators and the main scavenger species of the Southern Ocean (Hunter Reference Hunter, Siegfried, Condy and Laws1985). In the Antarctic, they breed mainly on offshore islands of the Antarctic Peninsula, with an estimated population of 5409 breeding pairs on the South Shetland Islands (Patterson et al. Reference Patterson, Woehler, Croxall, Cooper, Poncet, Hunter and Fraser2008). During the breeding season, the species uses pelagic, coastal and terrestrial environments of the Antarctic as foraging zones (Granroth-Wilding & Phillips Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019, Corá et al. Reference Corá, Finger and Krüger2020). During the non-breeding season, they use a much wider range of areas as their foraging grounds, including the high seas and the continental shelf of the south-west Atlantic and south-east Pacific (Krüger et al. Reference Krüger, Paiva, Finger, Petersen, Xavier, Petry and Ramos2018). In terrestrial zones, giant petrels usually concentrate in areas with penguin colonies (Copello et al. Reference Copello, Dogliotti, Gagliardini and Quintana2011) and breeding and haul-out sites of seals, where they feed on carrion or faeces (Corá et al. Reference Corá, Finger and Krüger2020). Sexes commonly have spatially segregated foraging areas to decrease intersexual competition, especially during the breeding season (González-Solís et al. Reference González-Solís, Croxall and Afanasyev2008, Granroth-Wilding & Phillips Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019). Females are mainly pelagic and feed primarily on marine prey, such as squid, fish and crustaceans, while males have a more coastal distribution and feed primarily on seabird and mammal carrion (Hunter Reference Hunter1983, Forero et al. Reference Forero, González-Solís, Hobson, Donázar, Bertellotti, Blanco and Bortolotti2005, González-Solís et al. Reference González-Solís, Croxall and Afanasyev2008, Copello et al. Reference Copello, Dogliotti, Gagliardini and Quintana2011). Both sexes have been found to be attracted to fishing vessels for the consumption of discards on the south Atlantic Ocean and Indian Ocean (Otley et al. Reference Otley, Reid, Phillips, Wood, Phalan and Forster2007, González-Solís et al. Reference González-Solís, Croxall and Afanasyev2008, Thiers et al. Reference Thiers, Delord, Barbraud, Phillips, Pinaud and Weimerskirch2014, Krüger et al. Reference Krüger, Paiva, Petry and Ramos2017). Due to their diverse habitat associations and top predator/scavenger position in the Antarctic trophic web, SGPs are a potential platform for monitoring the state of Antarctic populations and environments.
In this study, we show that, by continuously tracking movements of a single SGP population using GPS tracking devices, it is possible to assess a large array of areas and habitats along the Antarctic Peninsula. First, we describe foraging trip metrics and define foraging areas and important sites for the SGP population during reproduction using fine-scale GPS data and then run step-selection functions (SSFs) to identify which variables are responsible for sexes selecting a specific habitat, considering interindividual variability. Considering the known spatial and dietary segregation of the species, we expect males to make shorter trips, forage closer to the colony and be associated with penguin colonies and seal haul-out sites, and we expect females to make farther and longer trips, forage on productive, pelagic areas and, to a larger extent than males, to use areas with fishing activities.
Materials and methods
Tracking breeding southern giant petrels
Tracking data were obtained from SGPs breeding at Harmony Point, Nelson Island, Maritime Antarctica (62°18′S, 59°11′W). During the 2019–2020 and 2021–2022 seasons, 67 birds (33 females and 34 males) were tagged with GPS tracking devices: 18 were tracked with solar-powered GPS-UHF KITE-L devices (Ecotone Telemetry, 58 × 27 × 18 mm; 17 g), 4 with Axy-Trek Marine GPS loggers (TechnoSmArt, 40 × 20 × 8 mm; 14g), 8 with CatLog ThermoSeal GPS devices (Mr. Lee, 53 × 26 × 7 mm; 20 g), 16 with CatLog GPS devices with an epoxy-filled enclosure (Mr. Lee, 53 × 45 × 20 mm; 50 g) and 20 with BirdCam, a GPS device coupled to a small video camera (Mr. Lee, 70 × 26 × 17 mm; 24 g). KITE-L devices were attached using a backpack harness of tubular Teflon tape and the other devices were attached to dorsal feathers with 3M #2800 series duct tape and Loctite super glue. KITE-L and CatLog ThermoSeal devices were set to collect a fix every 5 min and Axy-Trek, BirdCam and CatLog epoxy devices were set to collect a fix every 10 min due to their lower battery capacity. KITE-L tracking data were downloaded to a local base station each time a bird returned to the colony following a foraging trip. Data from the other devices were downloaded following recapture at the end of the tracking period. Devices were removed from the birds by cutting supporting feathers with scissors. Birds were tracked for an average of 40.6 ± 8.9 days from 30 November 2019 to 25 January 2020 and for an average of 21.8 ± 6.9 days from 12 December 2021 to 25 January 2022. The tracking periods corresponded to the late egg incubation stage and the chick-rearing stage, the latter starting ca. 12 January.
Data processing
GPS data were filtered to remove locations at the nest. Due to data gaps and differences in fix sampling rates between devices, tracks were interpolated using the ‘track_resample’ function of the ‘amt’ R package (Signer et al. Reference Signer, Fieberg and Avgar2019) by resampling all locations to an equal 30 min interval, which was the highest median interval. Regular sampling rates are required for SSFs, because selection is not scale-invariant (Barnett & Moorcroft Reference Barnett and Moorcroft2007, Signer et al. Reference Signer, Fieberg and Avgar2017), and thus sampling rates should be similar for different individuals.
Trip metrics
To determine foraging trip characteristics, we split tracking data into individual foraging trips using the ‘tripSplit’ function in the ‘track2KBA’ R package (Beal et al. Reference Beal, Oppel, Handley, Pearmain, Morera-Pujol and Carneiro2021). We defined trips as periods of ≥ 1 h spent away from the colony at a distance of 250 m, since some individuals can make short trips and feed on seal faeces at the nearby glacier (Corá et al. Reference Corá, Finger and Krüger2020). We then calculated trip length (days), cumulative distance travelled between all locations (km) and maximum distance from the colony (km; hereafter ‘maximum range') using the ‘tripSummary’ function. Incomplete trips (unknown beginning or end dates) were removed from the analysis. The normality (Shapiro-Wilk test) and homoscedasticity (Bartlett test) of the data were verified before each statistical test. Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) with a penalized quasi-likelihood parameter estimation were used with trip metrics as response variables to assess differences between sexes, breeding stage and years. To incorporate the dependency among observations of the same individual, ID was used as a random intercept. We used a gamma error distribution with an inverse link function for cumulative distance and trip duration data and a Gaussian distribution with a log link function for maximum range data. We first evaluated whether a mixed model was necessary by running a linear model without a random effect (ID) and checking whether there was residual variance by plotting the residuals against the levels of ID. As residual variance was confirmed, we proceeded to select the most adequate mixed model by decreasing model complexity and comparing Akaike information criterion corrected for small sample sizes (AICc) values between models. Those with the highest AICc values were selected.
Estimating foraging areas
To visually identify geographical areas used by female and male SGPs, we computed 25%, 50%, 75% and 95% kernel utilization distributions (KUDs) for individuals of each sex using the ‘estSpaceUse’ function from the ‘track2KBA’ R package (Beal et al. Reference Beal, Oppel, Handley, Pearmain, Morera-Pujol and Carneiro2021). We used the scale of each sex's area-restricted search (ARS) as the kernel smoothing parameter (h), which was calculated using the ‘findScale’ function. Females had an ARS scale of 9.5 km and males of 9.0 km. As at-sea distribution changes according to the breeding stage and associated breeding duties (González-Solís et al. Reference González-Solís, Croxall and Afanasyev2008, Granroth-Wilding & Phillips Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019), we therefore estimated KUDs for incubation and chick-rearing stages separately. The 50% KUD is defined as the ‘core’ foraging area where birds spent 50% of their time (Ford & Krumme Reference Ford and Krumme1979, Soanes et al. Reference Soanes, Arnould, Dodd, Sumner and Green2013, Lascelles et al. Reference Lascelles, Taylor, Miller, Dias, Oppel and Torres2016). To ensure that data were representative of the foraging distribution of the colony-level population (~480 breeding pairs), we used a bootstrapping approach implemented in the ‘track2KBA’ R package (described in Lascelles et al. Reference Lascelles, Taylor, Miller, Dias, Oppel and Torres2016), which analyses the representativeness of the foraging areas as a function of sample size. Finally, we identified and delineated important sites for the population, which are areas used by a substantial portion of the population. We used the ‘findSite’ function that first calculates the proportion of individual core areas (i.e. % KUD areas) overlapping per grid cell. This proportion of overlapping tracks is then multiplied by the proportional representativeness of the tracked sample to adjust the sample-derived pattern by the degree of representativeness. The result is a scaled estimate of the proportion of the source population that predictably uses each grid cell in the study region during the season of interest.
Habitat characteristics
To assess characteristics of foraging habitats, we classified track points according to their speed and turning rate using the Expectation-Maximization Binary Clustering ('EmBC') R package (Garriga & Bartumeus Reference Garriga and Bartumeus2016). Foraging locations were defined as those with low speed (< 1.0 ms-1 ) and high turns (> 0.48 rad), parameters that characterize an intensive search behaviour. At these points, we extracted values of sea-surface chlorophyll a (which is a proxy for primary productivity), sea-surface temperature (SST), gradients of SST (SSTg; which indicate the positions of fronts more clearly), terrestrial and sea-ice concentration (SIC; referring to the proportion of the area that is covered by ice relative to open water, such as leads and polynyas), sea-bed depth and elevation (m; including both marine and terrestrial relief), distance from known penguin colonies (km) and distance from ice-free areas (km; which are potential unknown penguin colony sites or beaches used by seals as haul-out sites). Dynamic variables, except for ice concentration, were downloaded as December and January mean composite ‘netCDF’ files from Giovanni Browser (https://giovanni.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/). Chlorophyll a concentration (mg m-3) and SST at night (°C) were downloaded for a spatial resolution of 0.04° (~4 km). SIC (%) data were obtained as daily composites from the Sea Ice Remote Sensing Data browser - University of Bremen (Spreen et al. Reference Spreen, Kaleschke and Heygster2008, https://seaice.uni-bremen.de/databrowser/) as georeferenced .tiff images with a 6.25 km spatial resolution. Bathymetric data were obtained from the ETOPO1 Global Relief Model (www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/global/global.html) with a spatial resolution of 0.01° (~1 km). Penguin colony distribution was obtained from the Mapping Application for Penguin Populations and Projected Dynamics online database (MAPPPD; http://www.penguinmap.com). This dataset includes data on emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri), Adélie penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae), chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarcticus) and gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) colonies in Antarctica. Penguin colony distribution data in southern South America were obtained as published maps and then georeferenced in ArcMap 10.3 (ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA). Data were obtained for southern rockhopper penguins (Eudyptes c. chrysocome; Baylis et al. Reference Baylis, Wolfaardt, Crofts, Pistorius and Ratcliffe2013b), gentoo penguins (Baylis et al. Reference Baylis, Crofts and Wolfaardt2013a), king penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus; Pistorius et al. Reference Pistorius, Baylis, Crofts and Pütz2012) and Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus; Global Penguin Society; https://www.globalpenguinsociety.org/portfolio-species-15.html). Euclidean distances to penguin colonies were calculated with the Spatial Analyst tool in ArcMap 10.3. SST gradients were calculated as the standard deviation of SST in a 0.3° × 0.3° moving filter in Spatial Analyst. NetCDF files were first converted to raster files and then averaged into 2 month composites. Ice concentration data were first averaged into monthly composites and then averaged into a single mean composite for each summer. Each environmental variable was resampled to the same spatial grid of 0.06° (~6 km, the coarsest scale of the environmental datasets) to allow spatial comparison and combined modelling. All environmental variables were scaled using the ‘scale’ function in R. Processing of variables was done using the ‘raster’ R package (Hijmans & Van Etten Reference Hijmans and Van Etten2021).
As SGPs are known to interact with fisheries (Otley et al. Reference Otley, Reid, Phillips, Wood, Phalan and Forster2007, Jiménez et al. Reference Jiménez, Domingo, Abreu and Brazeiro2011), we obtained data on daily fishing effort (hours, all gear types) from the Global Fishing Watch database (https://globalfishingwatch.org) with a spatial resolution of 0.01° (~1 km). Fishing effort was only available for the 2019/2020 summer, and population-level overlap was too little to include this variable in the habitat selection analysis. We thus visually investigated the overlap of foraging areas (KUD 50%) and polygons of krill fishing areas obtained from Krüger et al. (Reference Krüger2019b) and with areas where toothfish (Dissostichus spp.) research-driven exploratory fisheries are allowed in Antarctica (Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR), https://gis.ccamlr.org/). Toothfish fishing usually occurs during periods of low sea-ice coverage, and its occurrence is evaluated on a yearly basis depending on the trends of toothfish populations (e.g. Hanchet et al. Reference Hanchet, Sainsbury, Butterworth, Darby, Bizikov and Rune Godø2015). Longline fishing effort is relatively low compared with longline fishing elsewhere (e.g. Clay et al. Reference Clay, Small, Tuck, Pardo, Carneiro and Wood2019), and, given the strict measures adopted for longline fishing in the area, seabird bycatch is also very low (Hanchet et al. Reference Hanchet, Sainsbury, Butterworth, Darby, Bizikov and Rune Godø2015, Collins et al. Reference Collins, Hollyman, Clark, Soeffker, Yates and Phillips2021). Therefore, the impact of toothfish fisheries is expected to be low and restricted within those areas. Krill fishing polygons encompass the summed area of fishing activity during the summers of 2013–2017. We also investigated whether SGP foraging areas were within confirmed marine Important Bird Areas (IBAs; BirdLife International, https://maps.birdlife.org/marineibas/), which are areas of significant importance for birds and therefore are priority areas for conservation.
Habitat selection
Habitat selection was evaluated as the probability of individuals choosing a specific step (two consecutive observed positions) among other available locations (random steps) in relation to the environmental covariates available within reach.
Firstly, geographical positions were translated into a step, which is composed of the step length and turning angle (deviation from previous bearings), using the ‘steps_by_burst’ function in the ‘amt’ R package. We then fitted gamma distributions to the step lengths and von Mises distributions to turn angles using maximum likelihood to generate nine random steps for each observed step based on these distributions (Signer et al. Reference Signer, Fieberg and Avgar2019). Random steps were generated using the ‘random_step’ function of the ‘amt’ R package. Environmental variables were extracted at the end of all steps to evaluate which variables were responsible for the animal choosing a specific habitat.
We then applied a SSF by fixing a mixed conditional Poisson model with individual-specific random slopes for each variable. We used steps of foraging points as the binary response variable (observed step = 1, random step = 0), environmental variables, stage and step length as covariates and individual ID as a random effect (following Muff et al. Reference Muff, Signer and Fieberg2020). We fixed the random effect variance to 106 because small values that could be selected by models tend to shrink the intercepts (Muff et al. Reference Muff, Signer and Fieberg2020). Models were run separately for each sex. Analysis was conducted in the glmmTMB R package (Brooks et al. Reference Brooks, Kristensen, Van Benthem, Magnusson, Berg and Nielsen2017), which uses a frequentist GLMM approach.
We used AICc model selection to distinguish among a set of candidate models describing the relationship between environmental variables, step length and step selection and the interaction between stage and environmental variables. The best-fit model for both was the most complex. Variables used in the final model were sea-surface chlorophyll a, SST, SSTg, distance from known penguin colonies, SIC and depth. Distance from ice-free areas was not included in the analysis as it was strongly correlated with distance from known penguin colonies (Pearson correlation, r = 0.73).
The probability of movement in relation to seal haul-out sites was not evaluated due to the lack of a complete dataset of these sites in the Antarctic Peninsula. However, the occurrence of SGPs on haul-out sites was verified by cross-checking Google Earth Pro satellite and drone imagery (only for Harmony Point) of terrestrial ice-covered areas overlapped by SGP foraging fixes. Cloud-free images of these sites, when existent, were inspected for the presence of seals, which can be identified as long black spots over the ice (LaRue et al. Reference LaRue, Rotella, Garrott, Siniff, Ainley and Stauffer2011). Drone images of Harmony Point were taken with a Mavic Pro II drone (DJI, Shenzhen, China) as part of another study (see Corá et al. Reference Corá, Finger and Krüger2020). Drone flight was authorized by a permit from Instituto Antártico Chileno (No. 1046/2019).
Results
We were able to recover 58 tags and retrieve data from 47 (21 in 2019–2020 and 26 in 2021–2022), a 70% data recovery rate success. Seven devices that were attached with tapes were lost, all of them attached to females. No device that was attached with a harness backpack was lost.
Foraging distribution and behaviour
A total of 34 complete foraging trips (13 from females and 21 from males) were obtained in 2019–2020 and 68 complete trips were obtained in 2021–2022 (26 from females and 42 from males). Individuals engaged in 1–14 days long trips between the Weddell and Bellingshausen seas and the southern tip of Tierra del Fuego, foraging up to ~2100 km away from the colony to the west of the Antarctic Peninsula, 1317 km to the south-east and 950 km to the north (Fig. 1). As expected, breeding stage and sex, but not individual ID and year (P = 0.303 and P = 0.301, respectively), influenced the maximum range, cumulative distance of trips and trip duration. Females tended to engage in longer foraging trips than males (Table I), both in the number of days (GLMM: t-value = 2.294, df = 34, P = 0.028) and in the maximum trip range (GLMM: t-value = -2.690, df = 34, P = 0.011) and had higher cumulative trip distances (GLMM: t-value = 3.041, df = 34, P = 0.004). For both sexes, incubation trips lasted longer (GLMM, days: t-value = -7.292, df = 34, P = 0.000) and reached greater distances (GLMM, maximum distance: t-value = -5.206, df = 34, P = 0.000) than in the chick-rearing stage (Fig. 1 & Table I).
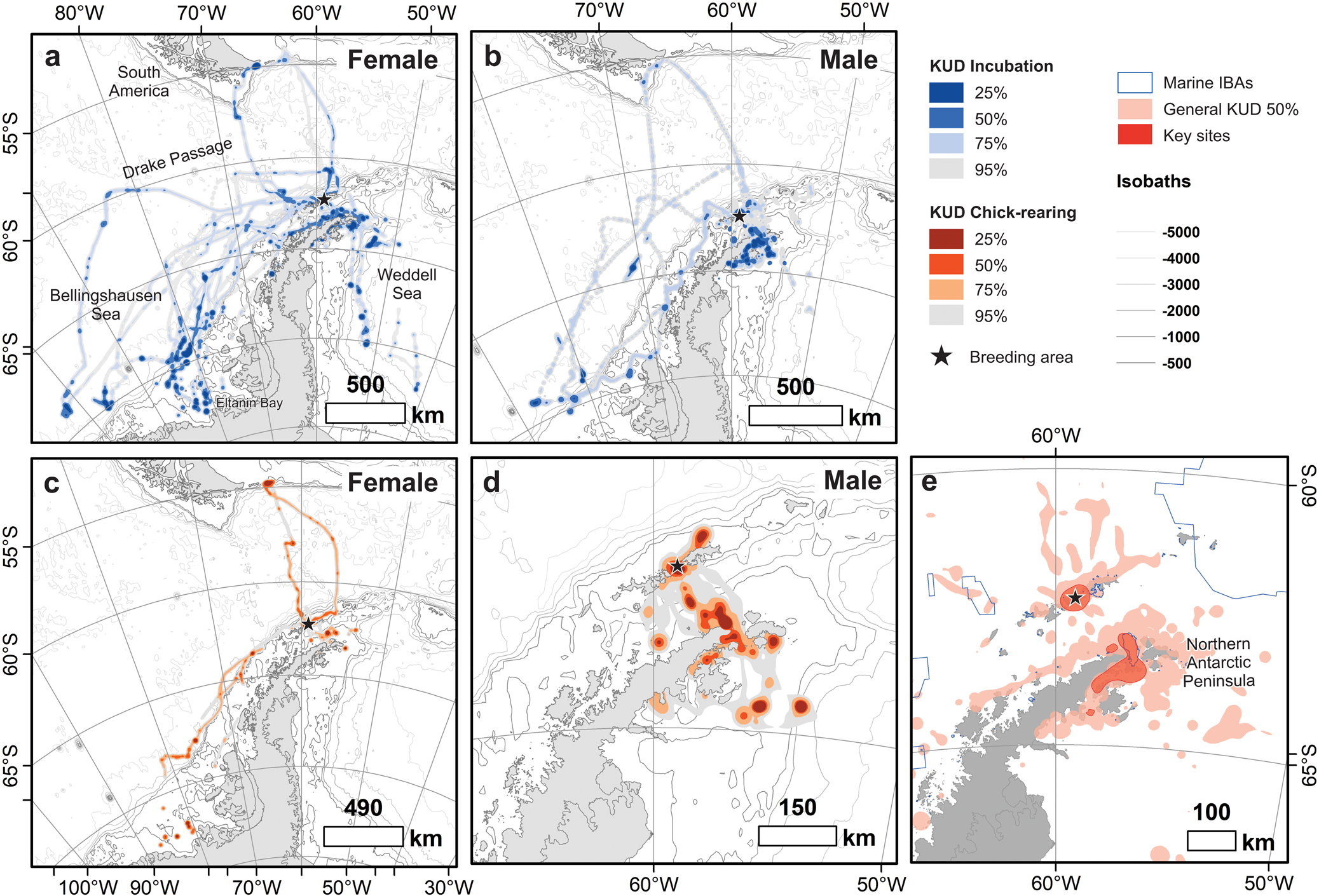
Fig. 1. Kernel usage density (KUD) of (a. & c.) female (n = 21) and (b. & d.) male (n = 26) breeding southern giant petrels (Macronectes giganteus) from Harmony Point, Nelson Island (black stars), tracked between December 2019 and January 2020 and between December 2021 and January 2022. Incubation and chick-rearing stages are depicted in blue and orange colours, respectively. Population-level 50% KUD and marine Important Bird Areas (IBAs; https://maps.birdlife.org/marineibas/) are depicted in e. Dark red polygons are key sites for the tracked population. Antarctic coastline polygons and bathymetric isolines were obtained from Gerrish et al. (Reference Gerrish, Fretwell and Cooper2021) and The International Bathymetric Chart of the Southern Ocean Version 2 (Dorschel et al. Reference Dorschel, Hehemann, Viquerat, Warnke, Dreutter and Schulze Tenberge2022), respectively.
Table I. Foraging trip metrics of breeding female and male southern giant petrels (n = 47). Results for metrics are given as median [quartile 1–quartile 3], with ranges given in parentheses.

Males fed extensively in the surroundings of their breeding colony, the nearby islands, the Bransfield Strait and the Trinity Peninsula, Graham Land (Fig. 1). Only one male foraged out of Antarctica, over waters to the south of Tierra del Fuego and in the same trip foraged up to -70°S (Fig. 1c). Females, despite also foraging near the colony and by the northern Antarctic Peninsula, showed a more widespread distribution, and many foraging locations were parallel to the Antarctic Peninsula. Eight females foraged south of -70°S in waters facing the Eltanin Bay in the Bellingshausen Sea and in the Weddell Sea. During incubation, one female reached longitude -103°W (Fig. 1a,b), travelling the farthest distance (2009.7 km from the colony) and covering the greatest cumulative distance (5293.5 km) of all individuals. The trip lasted 7.2 days.
Our estimates show that 96.2% of the core foraging areas (KUD 50%) used by the general Harmony Point population are captured by the sample of 47 tracked birds. Despite the variability in the foraging distribution, key areas for the species, which are areas used by a substantial portion of the population, are located around the breeding colony and by the tip of the northern Antarctic Peninsula and the Prince Gustav Channel, between Trinity Peninsula and James Ross Island (Fig. 1e). About a third of this key area is within IBA ‘Hope Bay Marine - Antarctic Sound', but it also overlaps with smaller IBAs, such as ‘Duroch Islands’ and ‘Devil Island’ (Fig. 1e).
Habitat selection
Water depth had a weak but positive effect (0.65) on male habitat selection, while distance from penguin colonies had a strong negative effect (-5.38). Water depth and the interaction between breeding stage and SIC had positive effects (0.76 and 0.75, respectively) on female habitat selection. Distance from penguin colonies and the interaction between stage and depth had negative effects (-1.03 and -0.75, respectively), meaning that, although with a weaker effect, females were also attracted by proximity to penguin colonies and to shallower waters during the chick-rearing stage (see Fig. 2).
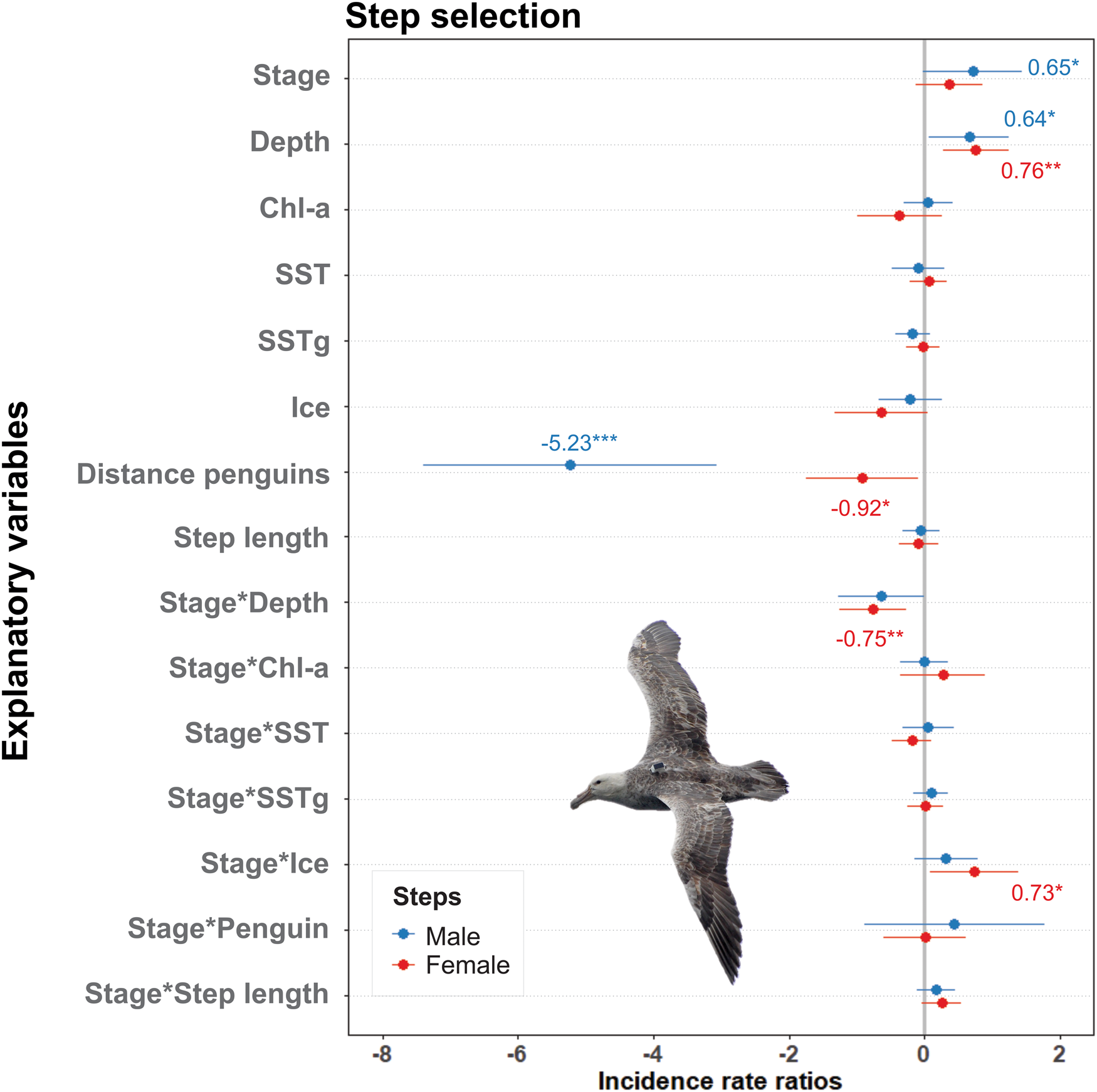
Fig. 2. Estimates and confidence intervals (95%) from the binomial step-selection model of breeding southern giant petrels. Significance codes: ***P = 0.001, **P = 0.01, *P = 0.05. Chl-a = chlorophyll a; SST = sea-surface temperature; SSTg = gradients of sea-surface temperature.
Males mainly selected areas with shallow to intermediate depths related to the coastal and continental shelf and foraged at shallower depths during the chick-rearing stage (Fig. 3a). They selected areas near penguin colonies with a median distance of 6.44 km during incubation and chick-rearing (see Figs 3c, 4c & 5). During incubation, females mainly selected areas with intermediate to deep depths related to the continental shelf, shelf slope and pelagic habitats, and, as with males, they foraged at shallower depths during the chick-rearing stage (Figs 1 & 3a). During incubation, females selected areas slightly more distant from penguin colonies than males (median: 20.37 km), but during chick-rearing the distance was similar (Fig. 3c). Although ice concentration alone had a negligible effect on habitat selection, both sexes used areas with varied ice concentrations (Fig. 3d), using habitats ranging from 0% to 99.8% ice coverage during incubation. Females tended to select habitats with markedly lower ice concentrations during chick-rearing (Fig. 3d).
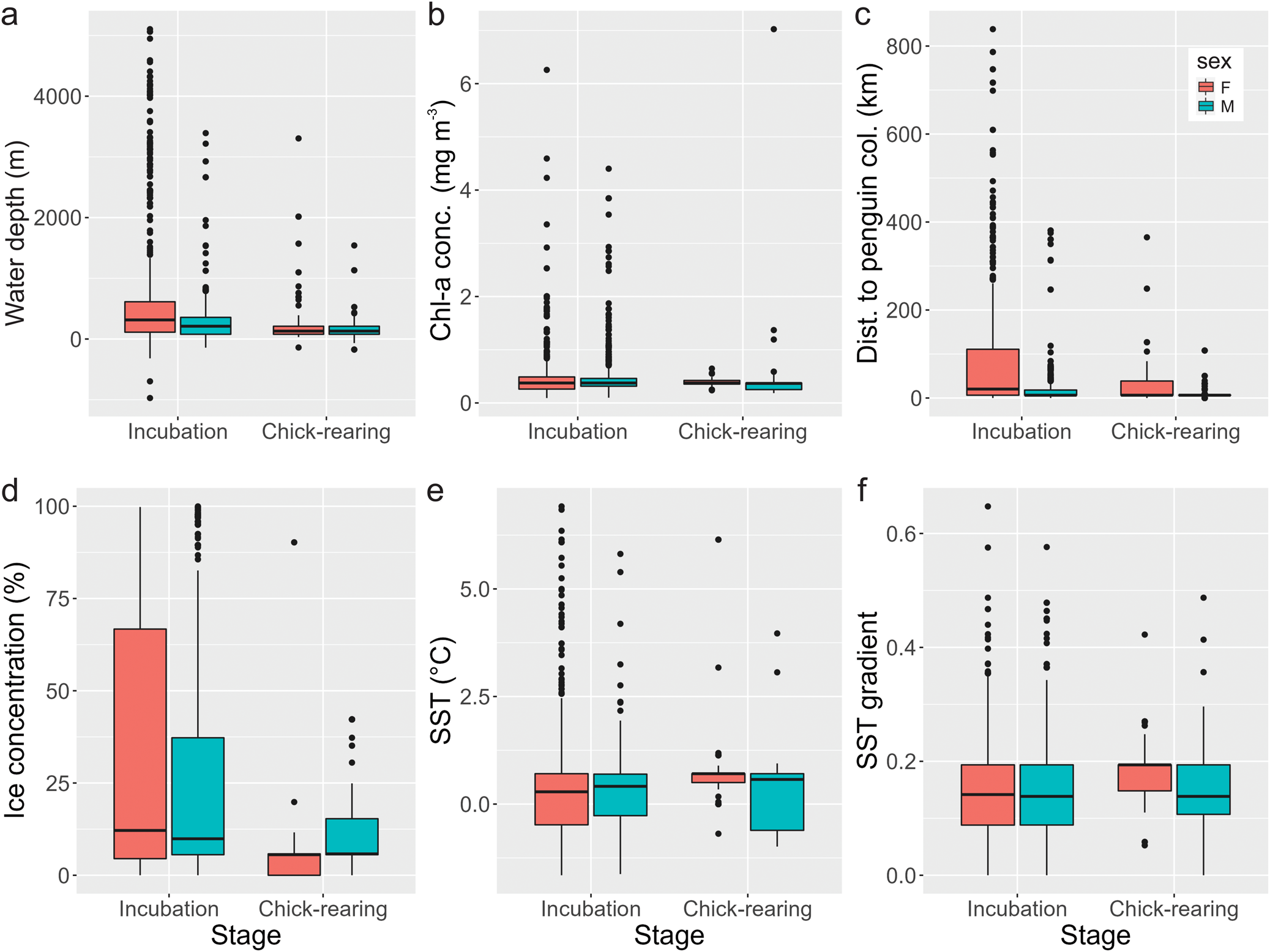
Fig. 3. Median values for the different environmental variables characterizing foraging areas of female (red) and male (blue) southern giant petrels from Nelson Island, Maritime Antarctica, during the incubation and chick-rearing stages. a. Water depth; b. chlorophyll a (Chl-a) concentration; c. distance to penguin colonies; d. sea-ice concentration; e. sea-surface temperature (SST); f. gradient of SST.
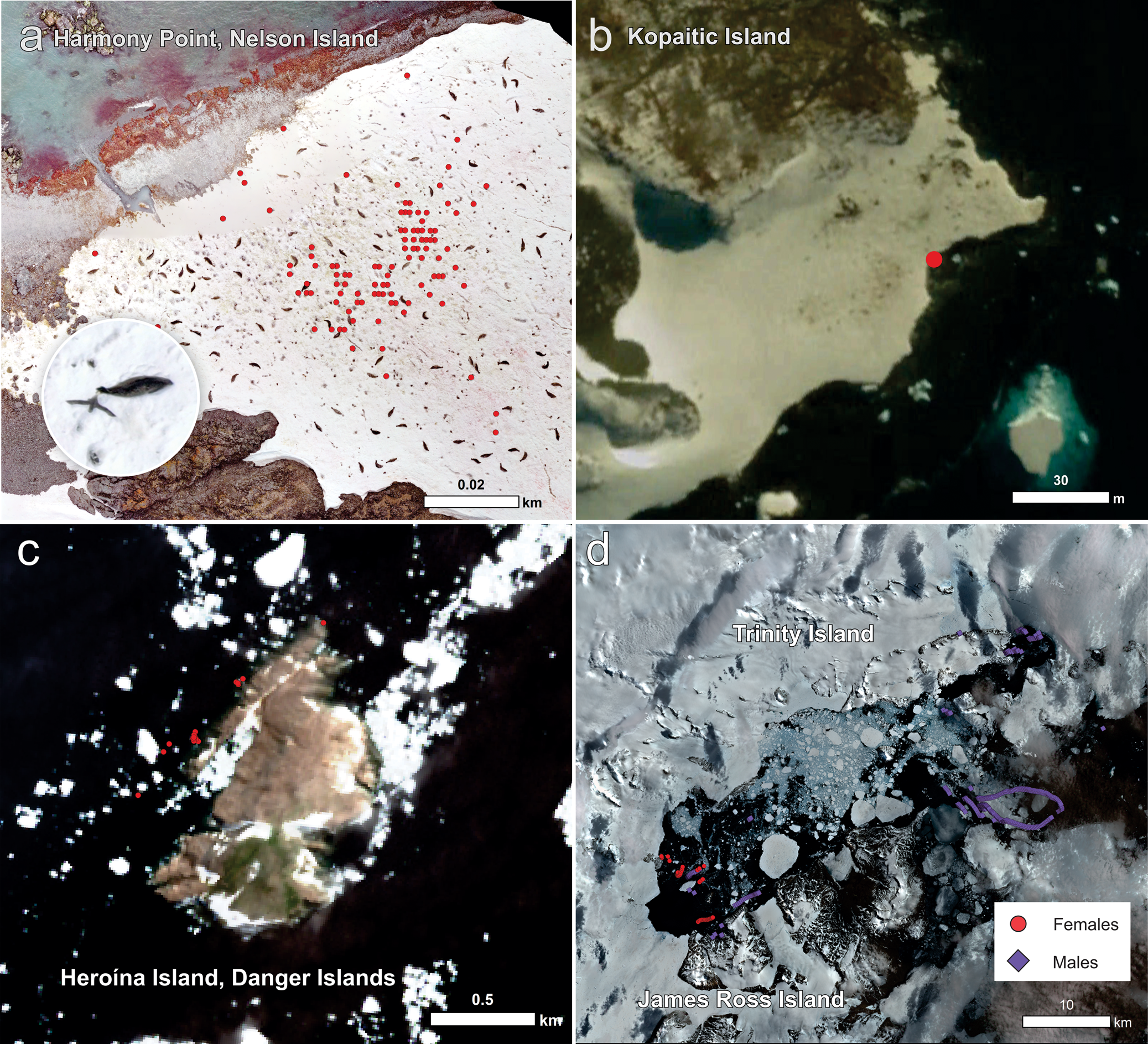
Fig. 4. Distinct habitats used by breeding southern giant petrels. a. Glacier edge at Harmony Point, Nelson Island, a haul-out site of Weddell seals (aerial drone image taken in January 2020); in detail is a southern giant petrel feeding on seal faeces. b. Ice-covered coast of Kopaitic Island where hauled-out seals are visible (Google Earth Pro image from 14 March 2015). c. Breeding colonies of Adélie penguins at Heroína Island (Danger Islands) in the Weddell Sea, where 292 363 breeding pairs were counted in 2015 (Borowicz et al. Reference Borowicz, Mcdowall, Youngflesh, Sayre-mccord, Clucas and Herman2018). d. Open water amid fast ice in the Prince Gustav channel, Weddell Sea (satellite image from 30 December 2019 freely obtained from Sentinel2, https://apps.sentinel-hub.com/eo-browser).

Fig. 5. Foraging areas (kernel usage density (KUD) 50%) of a. female and b. male southern giant petrels breeding at Harmony Point, Nelson Island, and the distribution of known penguin breeding colonies (Humphries et al. Reference Humphries, Naveen, Schwaller, Che-Castaldo, McDowall, Schrimpf and Lynch2017), confirmed marine Important Bird Areas (IBAs; BirdLife International, https://maps.birdlife.org/marineibas/), research blocks of exploratory toothfish (Dissostichus spp.) fisheries (Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR), https://gis.ccamlr.org/), areas used by Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) fisheries in recent years (Krüger Reference Krüger2019b) and longline fishing effort during December 2019 and January 2020 (Global Fishing Watch, https://globalfishingwatch.org).
Evidence of overlap between seal haul-out sites and foraging fixes of both sexes was found (Fig. 4a,b). At Harmony Point, where drone imagery allowed closer inspection, it was possible to determine that, when at land, birds frequently used ice-covered areas where Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) hauled out to rest (Fig. 4a).
There was also substantial overlap with areas consistently used by krill fisheries in previous years and exploratory toothfish fisheries, especially by females (Fig. 5). Overlap with toothfish fishery areas was mainly on research block 88.3_4 located over the Bellingshausen Sea and blocks 48.1_1, 48.1_2 and 48.1_3 on the Weddell Sea (Fig. 5a). One female and one male also overlapped their foraging range with areas with low fishing effort at the southern Patagonian Shelf slope, next to Isla de los Estados (Argentina), where trawlers and bottom longline vessels were fishing during the period when birds were using the area (Fig. 5a). The female foraged at this region during both the incubation and chick-rearing stage, while the male foraged there only during incubation.
Discussion
This study presented the fine-scale foraging distribution of a generalist marine top predator of the Antarctic, the SGP, and described its relationship with environmental variables during the breeding season. The survey, staged at Nelson Island, Maritime Antarctica, is the first to assess the fine-scale distribution of a SGP population breeding above 60°S.
Tracked birds used a wide area of the Antarctic Peninsula and adjacent islands, demonstrating that even by tracking a small number of individuals it is possible to assess conditions of a large area of the Antarctic, especially during the incubation period. The only previous tracking survey of SGPs breeding above 60°S was performed at Elephant Island (61°13′S, 55°21′W) using coarse-scale light-level geolocators (Krüger et al. Reference Krüger, Paiva, Petry and Ramos2017, Reference Krüger, Paiva, Finger, Petersen, Xavier, Petry and Ramos2018). SGPs from Elephant Island foraged mainly to the north of the island on the Drake Passage and less frequently in the northern Antarctic Peninsula. Birds from the present study, on the other hand, showed a marked southerly distribution in relation to their breeding colony (Nelson Island) and used a great share of the coast of the western and northern Antarctic Peninsula and the Bellingshausen and Weddell seas as foraging grounds, exploring ice-covered sea and land.
Previous studies tracking SGP populations across the Southern Ocean (e.g. Bird Island, South Georgia: González-Solís et al. Reference González-Solís, Croxall and Afanasyev2008, Granroth-Wilding & Phillips Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019; Argentine Patagonia, Copello et al. Reference Copello, Dogliotti, Gagliardini and Quintana2011; Crozet Island, Thiers et al. Reference Thiers, Delord, Barbraud, Phillips, Pinaud and Weimerskirch2014) in general showed that, during the breeding season, females made farther, longer and more pelagic trips than males and fewer coastal trips (Granroth-Wilding & Phillips Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019). This pattern is confirmed in the present study. Granroth-Wilding & Phillips (Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019) suggest that females use terrestrial and coastal areas to scavenge, which has been previously assumed as a male-dominated behaviour (Hunter Reference Hunter1983, González-Solís Reference González-Solís2004, Forero et al. Reference Forero, González-Solís, Hobson, Donázar, Bertellotti, Blanco and Bortolotti2005). The positive effect of proximity to penguin colonies on female habitat selection and consistent use of confirmed seal haul-out sites confirm this suggestion, but female coastal behaviour might also be related to coprophagy, a recently described behaviour for the species and specifically confirmed for the tracked population (Corá et al. Reference Corá, Finger and Krüger2020).
Males also showed a high probability of selecting foraging areas nearby penguin colonies. Males are known to actively predate on penguins (Le Bohec et al. Reference Le Bohec, Gauthier-Clerc, Gendner, Chatelain and Le Maho2003, Ryan et al. Reference Ryan, Sommer and Breytenbach2008) and adults and chicks of other seabirds on breeding colonies (Dilley et al. Reference Dilley, Davies, Connan, Cooper, De Villiers and Swart2013, Grohmann Finger et al. Reference Grohmann Finger, Corá, Petry and Krüger2021, Risi et al. Reference Risi, Jones, Osborne, Steinfurth and Oppel2021). It is possible to infer that some of the land areas visited by males, whose habitat selection was also positively influenced by water depth and elevation, could represent areas with an unknown presence of penguin colonies. Small penguin colonies are less likely to be spotted in satellite images (Fretwell & Trathan Reference Fretwell and Trathan2021) such as Sentinel2 (which has an open-source interface). Therefore, the foraging tracks of SGPs could provide clues as to where to invest field effort or where to use paid-for high-definition satellite images to verify the presence of small penguin colonies and to identify seal haul-out sites.
The same areas used by SGPs from Nelson Island have been identified as Areas of Ecological Significance (AESs) of the Southern Ocean (Hindell et al. Reference Hindell, Reisinger, Ropert-Coudert, Hückstädt, Trathan and Bornemann2020, fig. 1 of that study). Several confirmed marine IBAs (Fig. 5; https://maps.birdlife.org/marineibas/) were also visited, especially IBA ‘Hope Bay Marine - Antarctic Sound', which was created due to large foraging aggregations of breeding Adélie penguins. AESs are areas preferred by multiple predator species and indicate high levels of lower trophic biomass and biodiversity (Hindell et al. Reference Hindell, Reisinger, Ropert-Coudert, Hückstädt, Trathan and Bornemann2020). Due to their high productivity, they can also be targeted by fishing activities throughout the year (Fig. 4; Grémillet et al. Reference Grémillet, Ponchon, Paleczny, Palomares, Karpouzi and Pauly2018, Krüger Reference Krüger2019b). SGP mortality associated with longline fishery, although low, has been recorded outside Antarctica (Sullivan et al. Reference Sullivan, Reid and Bugoni2006, Gianuca et al. Reference Gianuca, Phillips, Townley and Votier2017). The consistent use of usual fishing areas in the southern Patagonian Shelf by breeding SGPs shows that even during the breeding season the species could be interacting with fishing boats outside the CCAMLR management areas. While seabird bycatch in longline fisheries has been reduced to a minimal within the CCAMLR areas due to strict measures and regulations (SC-CAMLR-40/BG/23, https://www.ccamlr.org/en/sc-camlr-40/bg/23), seabird mortality associated with krill fisheries (warp strikes and bycatch) has become a recent issue, with records of SGPs attending fishing nets and feeding on mammal bycatch (SC-CAMLR-40/BG/23, SC-CAMLR-40/BG/26, https://www.ccamlr.org/en/sc-camlr-40/bg/26, SC-CAMLR-40/BG/27, https://www.ccamlr.org/en/sc-camlr-40/bg/27). Krill fisheries have been recently changing their period of activity on the western Antarctic Peninsula towards the end of summer and early autumn (Krüger Reference Krüger2019b, Krüger et al. Reference Krüger, Huerta, Santa Cruz and Cárdenas2021); therefore, further data would be necessary to quantify any potential interaction of SGPs with krill fishing vessels. Although IUU longline fishing within the CCAMLR areas is currently not a great concern, unidentified fishing gear is retrieved from time to time (CCAMLR-40/06, https://www.ccamlr.org/en/ccamlr-40/06), indicating that such activity does occur. In this case, as IUU fisheries are unregulated, they might pose more risks to seabirds. SGPs, therefore, could be used as a means of monitoring any suspicious activity throughout the western Antarctic Peninsula; for instance, using the Automatic Identification Systems from vessels and radar detection tracking devices (Votier et al. Reference Votier, Bearhop, Witt, Inger, Thompson and Newton2010, Weimerskirch et al. Reference Weimerskirch, Collet, Corbeau, Pajot, Hoarau and Marteau2020) and bird-borne cameras (Votier et al. Reference Votier, Bicknell, Cox, Scales and Patrick2013).
Due to the large spatial scale of the Antarctic Peninsula, challenging field conditions and high logistical costs, monitoring the environment and the state and distribution of seabird and mammal populations is a challenge for researchers. In this sense, marine top predators have already been used as oceanographic platforms (Fedak Reference Fedak2013, Ohshima et al. Reference Ohshima, Fukamachi, Williams, Nihashi, Roquet and Kitade2013) and as indicators of past and current environmental change by tracking shifts in dietary (Carpenter-Kling et al. Reference Carpenter-Kling, Handley, Connan, Crawford, Makhado and Dyer2019), foraging (Miller & Trivelpiece Reference Miller and Trivelpiece2008), demographic (Trivelpiece et al. Reference Trivelpiece, Hinke, Miller, Reiss, Trivelpiece and Watters2011) and phenological parameters (Lynch et al. Reference Lynch, Fagan, Naveen, Trivelpiece and Trivelpiece2012). Optimal sentinel species should be conspicuous and easy to access and be sensitive and respond to changes in the environment in a timely and a detectable manner, which is usually associated with a reliance on a small diversity of or singular prey species (Hazen et al. Reference Hazen, Abrahms, Brodie, Carroll, Jacox and Savoca2019). SGPs are, however, a highly opportunistic and generalist species (Hunter Reference Hunter1984, Granroth-Wilding & Phillips Reference Granroth-Wilding and Phillips2019, Grohmann Finger et al. Reference Grohmann Finger, Corá, Petry and Krüger2021), whose status in Antarctica seems to be stable or increasing (e.g. Petry et al. Reference Petry, Valls, Petersen, Finger and Krüger2018, Krüger Reference Krüger2019a). Populations of the southern Atlantic Ocean, including the mid-latitudes of the Antarctic, have been favoured by climate change (Petry et al. Reference Petry, Valls, Petersen, Finger and Krüger2018, Gianuca et al. Reference Gianuca, Votier, Pardo, Wood, Sherley and Ireland2019) and the consumption of discards associated with increased fishing activity (Krüger et al. Reference Krüger, Paiva, Petry and Ramos2017). However, in a few sites, local population declines have been recorded and attributed to the stress caused by constant human activities, such as scientific activities and tourism (e.g. Nelson Island: Silva et al. Reference Silva, Favero, Casaux and Baroni1998; Signy Island: Conroy Reference Conroy1972). But as for populations breeding in higher latitudes or with more southerly breeding distributions, such as the one from Harmony Point, major causes of population variability are yet to be investigated. Therefore, although demographic studies of SGPs still might not be optimal tools for investigating environmental changes in the Antarctic, the large size, conspicuousness, accessibility of colonies and wide and diverse spatial distribution of SGPs make them useful monitoring platforms. Females can be particularly useful for investigating IUU fisheries, while both sexes can be used to investigate seal haul-out sites and penguin colonies. A long-term study joining GPS tracking, animal-borne cameras and diet analysis should provide researchers with a large amount of data on the condition and occurrence of penguin colonies, Weddell seal haul-out sites and IUU fisheries at different spatial and temporal scales.
Acknowledgements
We thank the logistics team from Instituto Antártico Chileno and Base Professor Julio Escudero and the crew of RS Karpuj, OPV Marinero Fuentealba and AP-41 Aquiles for transportation and logistical support. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions.
Financial support
This study was funded by Fondecyt (Fondecyt Iniciación 11180175), by the Marine Protected Areas Program of Instituto Antártico Chileno (INACH 2403052) and supported by ANID - Millennium Science Initiative Program - ICN2021_002. It was also partially financed by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) through a PhD scholarship to JVGF (Finance Code 001) and a master's scholarship to DHC (Finance Code 001).
Ethics approval
Animal study ethics were evaluated and approved by Instituto Antártico Chileno and the Comité Ético Científico de la Universidad de Magallanes. Entrance to Harmony Point Antarctic Specially Protected Area was authorized by Instituto Antártico Chileno (Permits No 1045/2019, No 662/2021 and No 433/2022). Sampling was authorized by Instituto Antártico Chileno (Permits No 1046/2019 and No 654/2021).
Author contributions
JVGF and LK conceived the ideas and designed the study; JVGF, LK and DHC collected the data; JVGF and LK analysed the data; JVGF led the writing of the manuscript. All authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.









