Introduction
Schizophrenia-like (SZ) psychoses and Parkinson's disease (PD) are both associated with dopaminergic dysfunctions in the corticobasal ganglia circuitry, and they both have a complex polygenic architecture involving numerous common variants conferring cumulative small effects towards developing the disorder. However, the dopaminergic abnormalities and associated clinical features point in two opposite directions in SZ and PD.
First, positive symptoms of SZ (i.e. delusions and hallucinations) are proposed to originate from excess dopamine activity in the nigrostriatal pathway and dorsal striatum (McCutcheon et al., Reference McCutcheon, Abi-Dargham and Howes2019), whereas the cardinal motor symptoms of PD (i.e. tremor, rigidity, postural instability and bradykinesia) are related to loss of dopaminergic neurons, or the presence of Lewy bodies in surviving neurons, in the substantia nigra pars compacta – which in turn causes striatal dopamine deficiency (Maiti et al., Reference Maiti, Manna and Dunbar2017).
Second, SZ treatment is based mainly on block or modulation of the dopamine D2 receptor (Kishi et al., Reference Kishi, Ikuta, Matsui, Inada, Matsuda, Mishima and Iwata2019), whereas PD treatment strategies aim to optimise nigrostriatal dopamine availability. Interestingly, recent report suggests that common genetic variants within the dopaminergic pathway (e.g. COMT and DRD3 genes) may increase individual susceptibility to develop psychotic symptoms secondary to dopaminergic treatment in PD (Redensek et al., Reference Redensek, Flisar, Kojovic, Gregoric Kramberger, Georgiev, Pirtosek, Trost and Dolzan2019).
Given the above, it is reasonable to hypothesise that, to some extent, the genetics of SZ and PD may underpin these opposing characteristics. In support of this hypothesis, we presented preliminary findings (Abstracts of the 26th World Congress of Psychiatric Genetics (WCPG): Quattrone et al., 2018) showing that, compared with population controls, first-episode psychosis (FEP) patients had a lower PD polygenic risk score (PRS), which was based on PD summary statistics covering 9830 risk variants (Chang et al., Reference Chang, Nalls, Hallgrimsdottir, Hunkapiller, van der Brug, Cai, Kerchner, Ayalon, Bingol, Sheng, Hinds, Behrens, Singleton, Bhangale and Graham2017). Hereby, we re-test the same hypothesis using full summary statistics from a recent larger PD genome-wide association study meta-analysis (Nalls et al., Reference Nalls, Blauwendraat, Vallerga, Heilbron, Bandres-Ciga, Chang, Tan, Kia, Noyce, Xue, Bras, Young, von Coelln, Simón-Sánchez, Schulte, Sharma, Krohn, Pihlstrom, Siitonen, Iwaki, Leonard, Faghri, Raphael Gibbs, Hernandez, Scholz, Botia, Martinez, Corvol, Lesage, Jankovic, Shulman, Sutherland, Tienari, Majamaa, Toft, Andreassen, Bangale, Brice, Yang, Gan-Or, Gasser, Heutink, Shulman, Wood, Hinds, Hardy, Morris, Gratten, Visscher, Graham and Singleton2019), expecting that an increased number of common risk variants for PD is negatively associated with the risk of developing FEP.
Methods and results
This analysis is based on genotyped FEP patients and population controls recruited across 17 study sites as part of the EUropean network of national schizophrenia networks studying Gene-Environment Interactions (EU-GEI). Study description was presented elsewhere (Di Forti et al., Reference Di Forti, Quattrone, Freeman, Tripoli, Gayer-Anderson, Quigley, Rodriguez, Jongsma, Ferraro, La Cascia, La Barbera, Tarricone, Berardi, Szöke, Arango, Tortelli, Velthorst, Bernardo, Del-Ben, Menezes, Selten, Jones, Kirkbride, Rutten, de Haan, Sham, van Os, Lewis, Lynskey, Morgan, Murray, Amoretti, Arrojo, Baudin, Beards, Bernardo, Bobes, Bonetto, Cabrera, Carracedo, Charpeaud, Costas, Cristofalo, Cuadrado, Díaz-Caneja, Ferchiou, Franke, Frijda, García Bernardo, Garcia-Portilla, González, Hubbard, Jamain, Jiménez-López, Leboyer, López Montoya, Lorente-Rovira, Marcelino Loureiro, Marrazzo, Martínez, Matteis, Messchaart, Moltó, Nacher, Olmeda, Parellada, González Peñas, Pignon, Rapado, Richard, Rodríguez Solano, Roldán Díaz, Ruggeri, Sáiz, Sánchez, Sanjuán, Sartorio, Schürhoff, Seminerio, Shuhama, Sideli, Stilo, Termorshuizen, Tosato, Tronche, van Dam and van der Ven2019). FEP patients were given standardised research-based diagnosis of psychotic disorders using the OPerational CRITeria checklist algorithm (OPCRIT) system (McGuffin et al., Reference McGuffin, Farmer and Harvey1991; Quattrone et al., Reference Quattrone, Di Forti, Gayer-Anderson, Ferraro, Jongsma, Tripoli, La Cascia, La Barbera, Tarricone, Berardi, Szoke, Arango, Lasalvia, Tortelli, Llorca, de Haan, Velthorst, Bobes, Bernardo, Sanjuan, Santos, Arrojo, Del-Ben, Menezes, Selten, Jones, Kirkbride, Richards, O'Donovan, Sham, Vassos, Rutten, van Os, Morgan, Lewis, Murray and Reininghaus2019).
Samples were genotyped at the MRC Centre for Neuropsychiatric Genetics and Genomics in Cardiff (UK) using a custom Illumina HumanCoreExome-24 BeadChip genotyping array covering 570 038 genetic variants. After genotype quality control, we excluded single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with minor allele frequency <0.5%, Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium p < 10−6 and missingness >2%. After sample quality control, we excluded samples with >2% missingness, heterozygosity F het > 0.14 or <−0.11 and subjects presenting genotype–phenotype gender mismatch. For the purposes of this analysis, we included only subjects who clustered into European ancestry at principal component analysis.
We performed imputation in the Michigan Imputation Server, using the Haplotype Reference Consortium reference panel with Eagle software for estimating the haplotype phase, and Minimac3 for genotype imputation (Das et al., Reference Das, Forer, Schonherr, Sidore, Locke, Kwong, Vrieze, Chew, Levy, McGue, Schlessinger, Stambolian, Loh, Iacono, Swaroop, Scott, Cucca, Kronenberg, Boehnke, Abecasis and Fuchsberger2016; Loh et al., Reference Loh, Danecek, Palamara, Fuchsberger, Reshef, Finucane, Schoenherr, Forer, McCarthy, Abecasis, Durbin and Price2016; McCarthy et al., Reference McCarthy, Das, Kretzschmar, Delaneau, Wood, Teumer, Kang, Fuchsberger, Danecek, Sharp, Luo, Sidore, Kwong, Timpson, Koskinen, Vrieze, Scott, Zhang, Mahajan, Veldink, Peters, Pato, van Duijn, Gillies, Gandin, Mezzavilla, Gilly, Cocca, Traglia, Angius, Barrett, Boomsma, Branham, Breen, Brummett, Busonero, Campbell, Chan, Chen, Chew, Collins, Corbin, Smith, Dedoussis, Dorr, Farmaki, Ferrucci, Forer, Fraser, Gabriel, Levy, Groop, Harrison, Hattersley, Holmen, Hveem, Kretzler, Lee, McGue, Meitinger, Melzer, Min, Mohlke, Vincent, Nauck, Nickerson, Palotie, Pato, Pirastu, McInnis, Richards, Sala, Salomaa, Schlessinger, Schoenherr, Slagboom, Small, Spector, Stambolian, Tuke, Tuomilehto, Van den Berg, Van Rheenen, Volker, Wijmenga, Toniolo, Zeggini, Gasparini, Sampson, Wilson, Frayling, de Bakker, Swertz, McCarroll, Kooperberg, Dekker, Altshuler, Willer, Iacono, Ripatti, Soranzo, Walter, Swaroop, Cucca, Anderson, Myers, Boehnke, McCarthy and Durbin2016).
We used PRSice (Euesden et al., Reference Euesden, Lewis and O'Reilly2015) to clump SNPs in approximate linkage disequilibrium and build the PRS, using the last available PD summary statistics as a base dataset (Nalls et al., Reference Nalls, Blauwendraat, Vallerga, Heilbron, Bandres-Ciga, Chang, Tan, Kia, Noyce, Xue, Bras, Young, von Coelln, Simón-Sánchez, Schulte, Sharma, Krohn, Pihlstrom, Siitonen, Iwaki, Leonard, Faghri, Raphael Gibbs, Hernandez, Scholz, Botia, Martinez, Corvol, Lesage, Jankovic, Shulman, Sutherland, Tienari, Majamaa, Toft, Andreassen, Bangale, Brice, Yang, Gan-Or, Gasser, Heutink, Shulman, Wood, Hinds, Hardy, Morris, Gratten, Visscher, Graham and Singleton2019). Briefly, we weighted individuals' risk variants in our dataset by the log odds ratio from the base dataset and sum them into PD PRS.
We used logistic regression to test for association between PD PRS and FEP status, after covarying for five ancestry principal components, sex, age and study site. Using PRSice, we tested the PRS for association, building PRS based on risk alleles defined at multiple p-value thresholds (for association with PD). We then selected the specific PRS which maximised the variance in the FEP-control status, controlling for multiple testing by randomly resampling the case-control phenotype over 10 000 permutations and repeating the PRSice procedure to get an empirical distribution for the p value at the maximised PRS (Euesden et al., Reference Euesden, Lewis and O'Reilly2015). Significance was calculated as the proportion of permutations in which no p value at any tested p value threshold (not just the specific maximised one) was less that the optimised p value obtained from PRSice in the real data. Finally, we used the Additive Variance Explained and Number of Genetic Effects Method of Estimation (AVENGEME) method to estimate the genetic covariance (σ12) between target and base samples (Palla and Dudbridge, Reference Palla and Dudbridge2015).
Principal component analysis for population stratification showed that N = 1127 individuals clustered into European ancestry (N FEP = 423; N controls = 704). The most common diagnoses at FEP were schizoaffective disorders (38%) and SZ (34%), followed by unspecified non-organic psychotic disorder (18%), bipolar disorder (5%) and psychotic depression (4%).
Logistic regression indicated that, at the SNPs Pt-threshold of 0.008 (N SNPs = 24 241), PD PRS was negatively associated with the risk of developing FEP [OR 0.79 (95% CI 0.69–0.92)] (Fig. 1). This association survived after permutation analysis (p value = 0.003; empiric p value = 0.047). Finally, a negative genetic covariance was observed between our sample and PD summary statistics [σ12 = −0.04 (95% CI −0.06 to −0.03)].
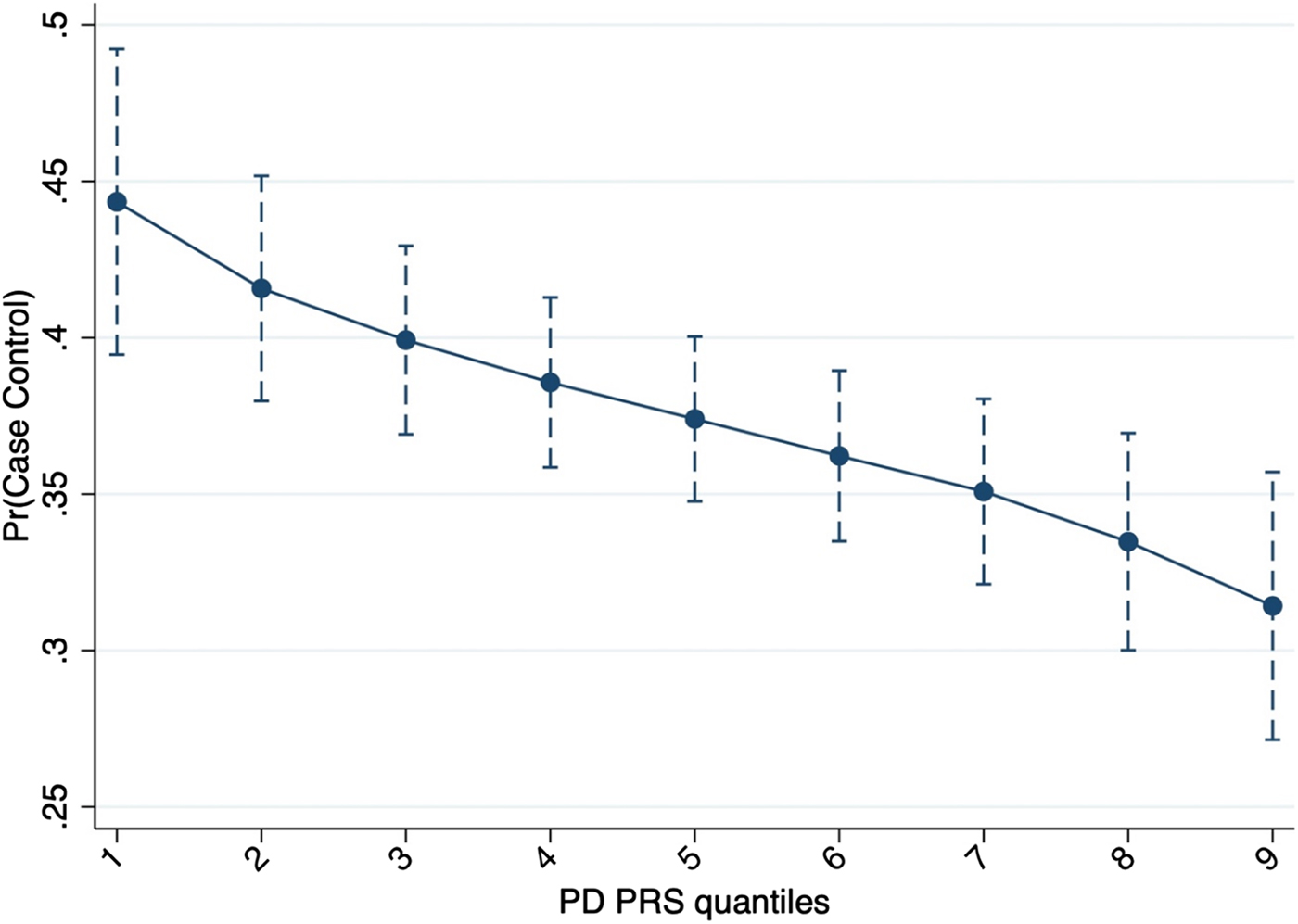
Fig. 1. Probability to be a case based on PD PRS including 24 241 genetic variants.
Discussion
In addition to the differences between SZ and PD, there are also some similarities. For example, non-motor features in PD may include positive and negative psychotic symptoms (Schapira et al., Reference Schapira, Chaudhuri and Jenner2017), whereas non-psychotic symptoms in SZ may include motor abnormalities (Koning et al., Reference Koning, Tenback, van Os, Aleman, Kahn and van Harten2010). Positive psychotic symptoms in PD were formerly thought to occur in a late stage, as adverse effects of levodopa or dopamine agonist treatments. However, it has been showed that hallucinations can precede clinical diagnosis of PD, which is usually given after 50–60% of dopaminergic neurons are lost. Before that, patients can experience early signs and symptoms thought to be related to dopaminergic dysfunction, such as hyposmia, vision disturbances, impaired colour vision, pain, anxiety, depression, early cognitive dysfunction, sleep disorders and bladder hyperreflexia (Schapira et al., Reference Schapira, Chaudhuri and Jenner2017). From a phenomenological perspective, hallucinations in PD drug-naïve patients are usually of visual nature (Pagonabarraga et al., Reference Pagonabarraga, Martinez-Horta, Fernandez de Bobadilla, Perez, Ribosa-Nogue, Marin, Pascual-Sedano, Garcia, Gironell and Kulisevsky2016) and they may be linked to abnormal visual processing or Rapid Eye Movement sleep behaviour disturbances. Noteworthily, the prevalence of visual hallucinations across the course of PD might be correlated with dopamine receptor gene variants (Ferrari et al., Reference Ferrari, Comi, Marino, Magistrelli, De Marchi, Cantello, Riboldazzi, Bono and Cosentino2016).
Limitations in the current analysis are the relatively small target sample size. Further, we could not test if SZ PRS is negatively associated with the PD status in an independent PD-population control sample. Bearing in mind these limitations, our results suggest that, in our sample (1) common genetic variants might contribute to the mechanisms underlying SZ and PD, mostly having opposite direction effects; and (2) FEP patients have lower polygenic risk for PD compared with population controls.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by: Clinician Scientist Medical Research Council fellowship (project reference MR/M008436/1) to MDF; National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre for Mental Health at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The EU-GEI Project is funded by the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme under grant agreement No. HEALTH-F2-2010-241909 (Project EU-GEI).



