Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2021
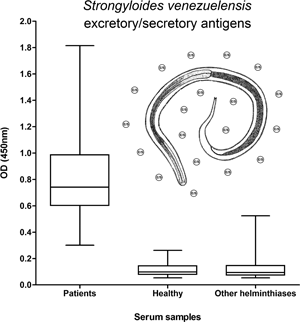
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of three types of antigenic preparations from Strongyloides venezuelensis infective larvae for detection of serum IgG anti-Strongyloides antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Soluble somatic fractions (SSF) and membrane somatic fractions (MSF) and excretory−secretory (E/S) products from S. venezuelensis infective larvae were evaluated against 71 sera from individuals with strongyloidiasis, 105 sera from healthy individuals, and 84 sera from individuals with other helminth infections. Using an ELISA cut-off for 100% sensitivity, E/S products were 97.88% specific followed by MSF (93.12%) and then by SSF (85.2%). The occurrence of cross-reactivity with other helminths was 4.76% (4/84) with E/S products, 8.33% (7/84) with MSF, and 17.86% (15/84) with SSF. For a cut-off for 100% specificity, E/S products showed a sensitivity of 88.73% whereas MSF and SSF showed sensitivities of 59.15% and 53.52%, respectively. In conclusion, E/S products were the best antigenic option for the serodiagnosis of human strongyloidiasis.