No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 November 2020
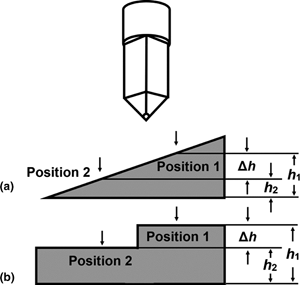
The thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) is a vital design parameter for reducing the thermal-stress-induced structural failure of electronic chips/devices. At the micro- and nano-scale, the typical size range of the components in chips/devices, the CTEs are probably different from that of the bulk materials, but an easy and accurate measurement method is still lacking. In this paper, we present a simple but effective method for determining linear CTEs of micro-scale materials only using the prevalent nanoindentation system equipped with a heating stage for precise temperature control. By holding a constant force on the sample surface, while heating the sample at a constant rate, we measure two height–temperature curves at two positions, respectively, which are close to each other but at different heights. The linear CTE is obtained by analyzing the difference of height change during heating. This method can be applied to study the size effect or surface effect of CTE of embedded micro-scale structures, aiding the failure analysis and structural design in the semiconductor industry.