Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 October 2018
Manifestly Markovian closures for the interaction of two-dimensional inhomogeneous turbulent flows with Rossby waves and topography are formulated and compared with large ensembles of direct numerical simulations (DNS) on a generalized 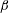 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$-plane. Three versions of the Markovian inhomogeneous closure (MIC) are established from the quasi-diagonal direct interaction approximation (QDIA) theory by modifying the response function to a Markovian form and employing respectively the current-time (quasi-stationary) fluctuation dissipation theorem (FDT), the prior-time (non-stationary) FDT and the correlation FDT. Markov equations for the triad relaxation functions are derived that carry similar information to the time-history integrals of the non-Markovian QDIA closure but become relatively more efficient for long integrations. Far from equilibrium processes are studied, where the impact of a westerly mean flow on a conical mountain generates large-amplitude Rossby waves in a turbulent environment, over a period of 10 days. Excellent agreement between the evolved mean streamfunction and mean and transient kinetic energy spectra are found for the three versions of the MIC and two variants of the non-Markovian QDIA compared with an ensemble of 1800 DNS. In all cases mean Rossby wavetrain pattern correlations between the closures and the DNS ensemble are greater than 0.9998.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$-plane. Three versions of the Markovian inhomogeneous closure (MIC) are established from the quasi-diagonal direct interaction approximation (QDIA) theory by modifying the response function to a Markovian form and employing respectively the current-time (quasi-stationary) fluctuation dissipation theorem (FDT), the prior-time (non-stationary) FDT and the correlation FDT. Markov equations for the triad relaxation functions are derived that carry similar information to the time-history integrals of the non-Markovian QDIA closure but become relatively more efficient for long integrations. Far from equilibrium processes are studied, where the impact of a westerly mean flow on a conical mountain generates large-amplitude Rossby waves in a turbulent environment, over a period of 10 days. Excellent agreement between the evolved mean streamfunction and mean and transient kinetic energy spectra are found for the three versions of the MIC and two variants of the non-Markovian QDIA compared with an ensemble of 1800 DNS. In all cases mean Rossby wavetrain pattern correlations between the closures and the DNS ensemble are greater than 0.9998.